8/18/2025 | 9 Minute Read
Topics:

Email remains one of the most common and effective attack vectors for cyber criminals, and artificial intelligence is making those attacks more convincing than ever. Spam and phishing emails often appear similar at first glance, but the risks they pose are fundamentally different. Spam clutters inboxes with irrelevant or unsolicited messages. Phishing, on the other hand, is a targeted cyberattack designed to steal credentials, deliver malware, or impersonate trusted contacts. AI is now being used to craft more realistic, scalable phishing campaigns.
Understanding the difference between spam and phishing is essential to maintaining strong email security. With the right mix of AI-powered filtering tools, phishing protection, and cybersecurity awareness training, organizations can reduce risk and better defend users from both low-risk nuisances and high-impact threats.
Spam is an unsolicited, irrelevant email, usually sent in bulk for marketing, advertising, or low-effort scam purposes. These messages often promote questionable products, redirect users to shady websites, or flood inboxes with repetitive, low-quality content. While spam is typically not as dangerous as phishing, it can still drain productivity and serve as a distraction, or even act as a launchpad for more targeted attacks.
Common characteristics of spam emails include:
From an email security perspective, spam is considered low to moderate risk. However, modern email threat protection tools are essential to identify subtle patterns in sender behavior, message structure, and metadata, filtering out spam before it reaches the inbox and reducing alert fatigue for users.
Phishing is a form of cyberattack that uses deceptive emails to trick recipients into sharing sensitive information, clicking on malicious links, or downloading infected attachments. Unlike spam, phishing emails are often carefully crafted to look legitimate, impersonating trusted brands, coworkers, or service providers.
Phishing emails often:
Phishing remains one of the most serious threats to cybersecurity. AI phishing threats are on the rise, with attackers using AI to scale spear phishing, which are phishing attacks directed at an individual instead of mass delivery. In addition, AI can help attackers mimic tone and writing styles and generate sophisticated campaigns that are harder to detect.
Effective phishing email protection now requires:
Even one AI-enhanced phishing email slipping past traditional filters can result in ransomware, data loss, financial theft, and regulatory penalties. That’s why phishing prevention is so critical and modern email protection strategies must evolve as quickly as the threats themselves.
While both spam and phishing involve unwanted emails, their intent, risk level, and sophistication are significantly different. The rise of AI-generated phishing emails has made it more important than ever to understand these distinctions. Cybercriminals are now using generative AI to craft realistic emails, mimic writing styles, and even automate spear-phishing campaigns at scale.
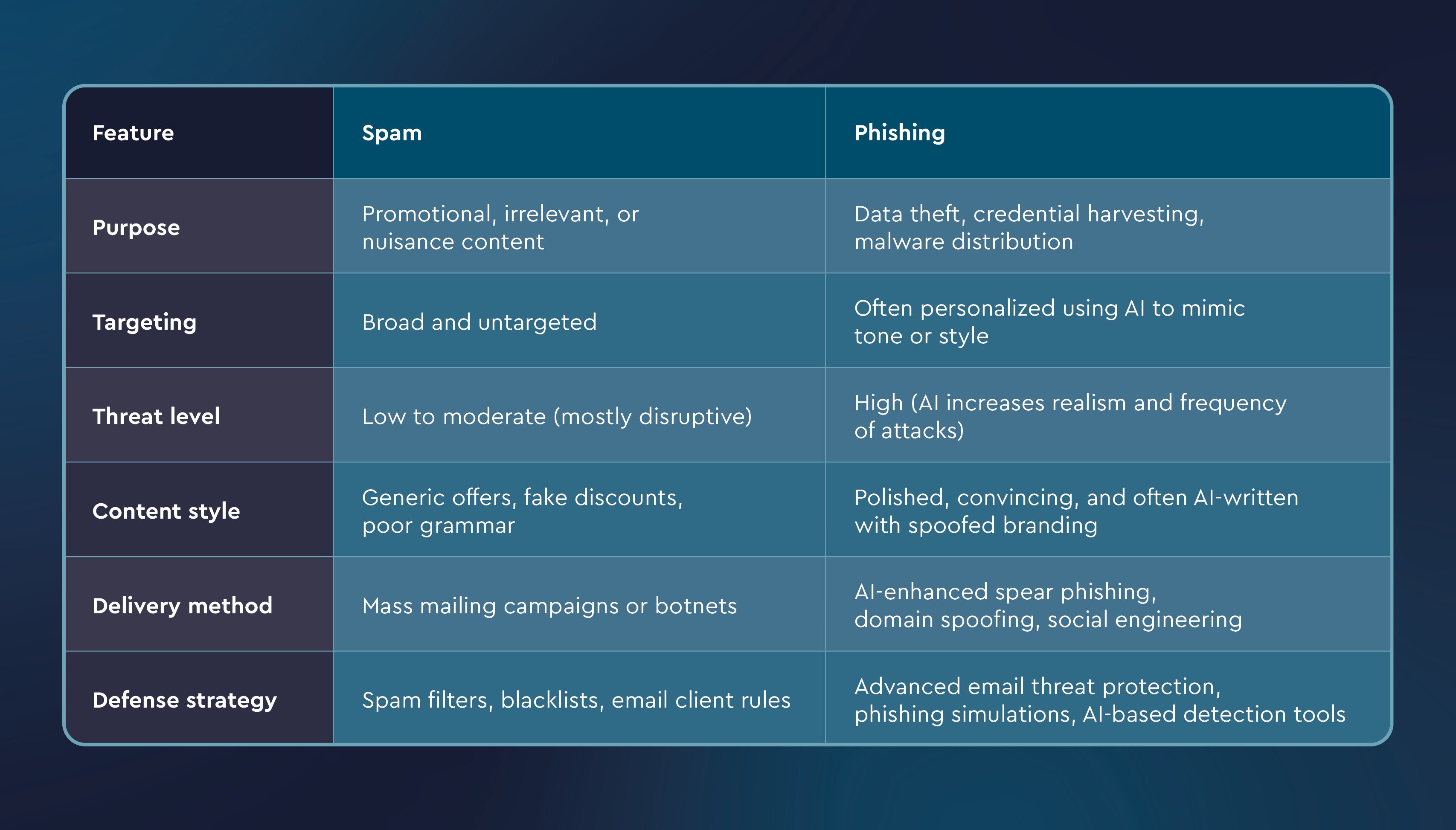
Spam and phishing both impact email systems, but AI-powered phishing emails raise the threat to a new level. Once-easy-to-spot indicators, such as misspelled sender names or broken formatting, have evolved into natural-sounding, believable communication generated with AI.
Spam risks:
Phishing risks:
Organizations need multi-layered email protection that combines threat detection, AI-based filtering, and employee training to defend against both types of email threats.
Email security is only as strong as its weakest link, and in most organizations, that link is the end user. Even the most advanced filtering tools can’t block every malicious message, especially as cybercriminals use AI to generate more convincing phishing emails that slip past traditional defenses.
That’s why cybersecurity awareness training is essential. It equips employees with the knowledge to spot and report phishing attempts, reducing the likelihood that a single mistake will lead to a breach. With attackers using AI to craft highly personalized, realistic emails, organizations can’t afford to rely solely on technology. The human layer must be just as prepared.
Effective training helps users identify:
AI-generated phishing attacks have made it easier for bad actors to scale and automate deception. What once took hours to craft can now be generated in seconds, making every inbox a potential entry point. Without training, users are far more likely to become the weakest link in your security chain.
To strengthen this link, organizations need ongoing cybersecurity awareness training that includes:
By turning your employees into active defenders rather than passive targets, you dramatically reduce your exposure to phishing and email-based threats, even those enhanced by AI. Training transforms the weakest link into a resilient human firewall.
Spam and phishing emails may seem similar at a glance, but the threats they pose are very different. Spam clutters inboxes and distracts users, while phishing, especially when powered by AI, is designed to deceive, steal, and compromise. As email threats evolve, so must your defenses.
ConnectWise offers a full suite of cybersecurity and data protection solutions designed to help MSPs and IT teams protect their clients from every angle, including email-based threats. Through our strategic partnership with ProofPoint, ConnectWise delivers
In addition to email threat protection, ConnectWise helps strengthen your overall posture with:
By combining technology, education, and visibility, ConnectWise enables you to stop threats before they reach users and turn your team’s weakest link into a resilient first line of defense.
Spam emails are bulk, unsolicited messages, usually for advertising or scams, that clutter inboxes but are typically low risk. Phishing emails are malicious and intentionally crafted to trick users into revealing sensitive information, installing malware, or granting unauthorized access. Phishing often uses social engineering and, increasingly, AI to appear legitimate.
Yes. AI is now used to create more convincing phishing emails by mimicking brand language, generating natural-sounding messages, and scaling targeted attacks. This makes phishing harder to detect and increases the likelihood that users will fall for the scam.
Protecting your organization requires a multi-layered email security strategy that includes AI-powered filtering, secure email gateways, phishing simulations, and cybersecurity awareness training. It’s also important to regularly update detection tools and educate employees on how to spot malicious messages.
Employees are often the weakest link in email security. Cybersecurity awareness training teaches users how to recognize spam, avoid phishing scams, and report suspicious messages. When combined with phishing simulations, this training significantly reduces the risk of human error.
ConnectWise Email Security™ with ProofPoint provides comprehensive inbox and user protection, including phishing simulations and email threat protection. These tools help MSPs and IT teams block malicious messages and train users to defend against evolving threats.