Successful cybercrime attacks often take groups of individuals working together. Some are extremely organized cybercrime syndicates such as the Conti group, but often individual criminals provide services to other criminals as vendors operating through a marketplace. Ransomware-as-a-Service (RaaS) or Botnet-as-a-Service (BaaS) providers regularly advertise their services on forums such as Exploit or XSS and setup affiliate programs. One type of service that can be found within the cybercrime ecosystem is the initial access broker (IAB).
An initial access broker is a threat actor, individual or group, that focuses on gaining remote access to their victims’ networks and systems. They then sell that access on various dark web or special-access sites to other threat actors who have their own goals such as stealing data or deploying ransomware. The type of access IABs sell typically include credential pairs for services such RDP, VPNs, corporate email accounts and more. Access to systems compromised by zero-day and n-day vulnerabilities are also available for sale.
IABs frequently rent access from malware-as-a-service (MaaS) and botnet-as-a-service (BaaS) threat actors through various cybercrime markets and forums to deploy infostealing malware such as Vidar, Redline, AZORult, and others. The infostealer malware is typically distributed via phishing or malicious ad campaigns. Once infected, infostealers attempt to gain access to cached credentials in memory or in the victim’s browser or may deploy a keylogger. They then connect back to the BaaS or MaaS provider’s command and control (C2) infrastructure with the stolen data.
Darknet markets and cybercrime forums come and go regularly and are often full of as many scam artists as actual IABs. It is not unheard of for an ad for credentials, credit cards, or other stolen data on one of these cybercrime sites to be fake. So, the most popular and successful of these sites employ several safeguards for their users. Typically, a marketplace such as this will rely on customer feedback and reviews just like you might find on normal, legitimate online marketplaces. The marketplace itself often holds money used in transaction in escrow until both sides confirm the deal completed satisfactorily. If a dispute arises between a vendor, such as an IAB, and their customer, such as a ransomware affiliate, the moderators of the marketplace act as mediators to resolve the dispute. For example, below is a screenshot from a recent report by Insikt Group of an ad for a credible IAB known as “inthematrix1”.
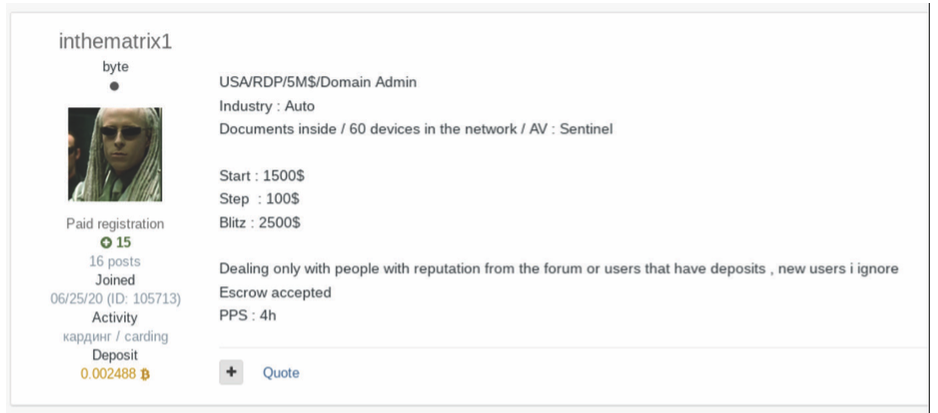
We can see from the user’s profile summary on the left, that “inthematrix1” has been a member of this marketplace since June 25, 2020, has made a total of 16 posts, and has completed 15 transactions successfully. We also see that they currently have 0.002488 bitcoin (approximately $60 as of today) currently deposited with the forum.
On July 18, 2022, an IAB going by the username “Beeper” posted an ad on Exploit advertising they have access to an MSP and were looking for a “partner”, most likely referring to a ransomware affiliate, to work with. Below is a screenshot of that post:
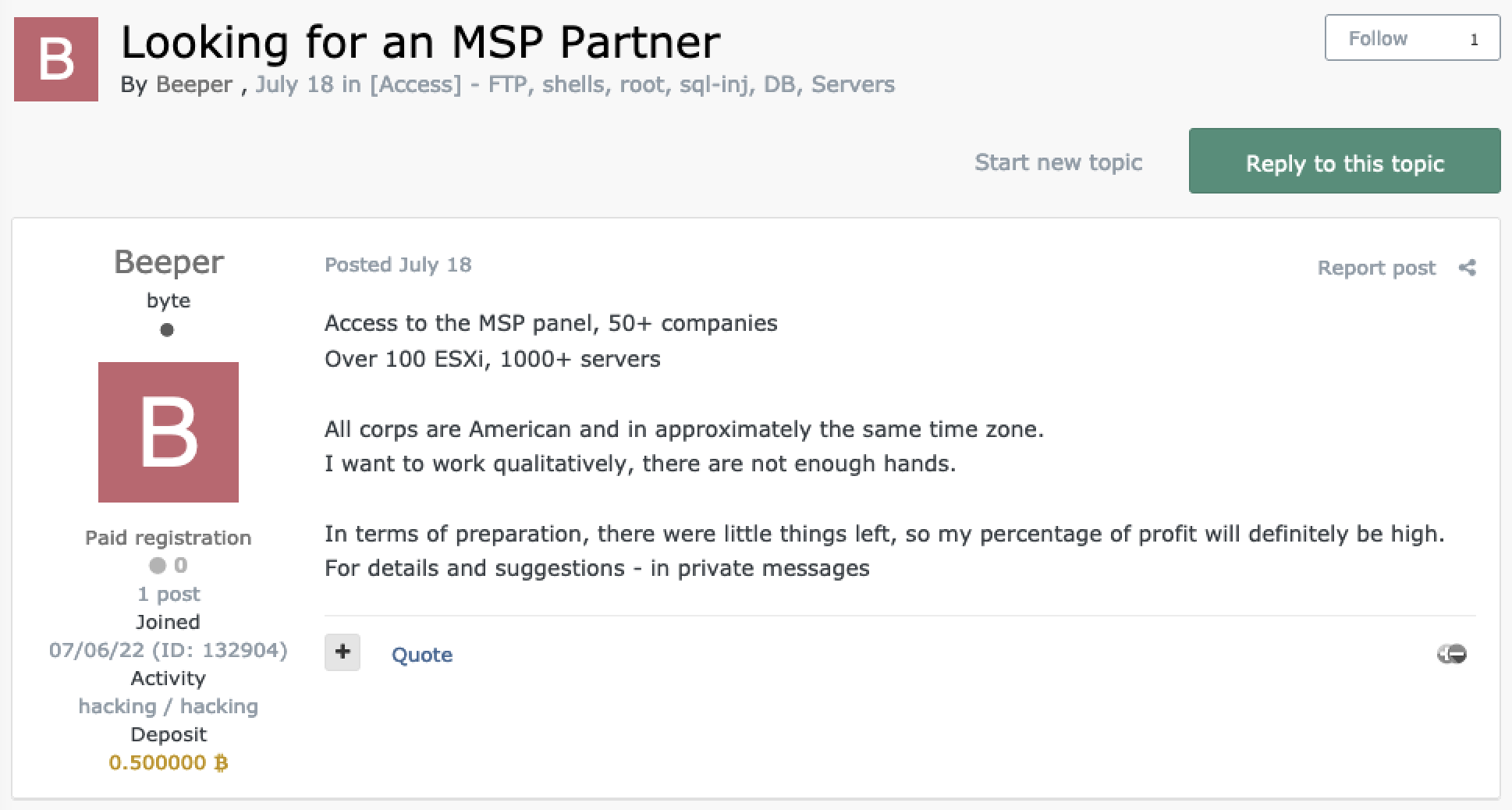
We can see from this IABs profile summary on the left that they are a new user who has only made a single post, the one above, with no positive feedback. They do, however, have 0.5 BTC deposited (approximately $11,700 as of today). The original ad above by Beeper was posted on July 18, and as of today, August 3, Beeper has not made any additional posts nor received any feedback. Though they have some money deposited to the forum, they would still be considered a risky vendor by most threat actors to the age of the account, no reputation, and no other posts. It can take time for a new IAB to build credibility, typically starting with smaller transaction and building up a reliable history. And even though they have 0.5 BTC deposited, keep in mind that for an attack on the scale advertised, the ransom could potentially net millions.
As we mentioned in our 2022 MSP Threat Report, 2021 MSP Threat Report and the 2020 MSP Threat Report MSPs are increasingly becoming high priority targets for threat actors. We also pointed out in the 2022 report that phishing and stolen credentials are still the most common methods used by threat actors to gain initial access. The Insikt report mentioned above also points out that phishing is still one of the most common methods IABs use to deploy infostealers. We’ve said it before and we’ll probably say it again, MSPs can significantly reduce their attack surface by implementing common mitigations such as email filters, user training, password hygiene, and MFA everywhere.






